About us
Learn how GA4GH helps expand responsible genomic data use to benefit human health.
Learn how GA4GH helps expand responsible genomic data use to benefit human health.
Our Strategic Road Map defines strategies, standards, and policy frameworks to support responsible global use of genomic and related health data.
Discover how a meeting of 50 leaders in genomics and medicine led to an alliance uniting more than 5,000 individuals and organisations to benefit human health.
GA4GH Inc. is a not-for-profit organisation that supports the global GA4GH community.
The GA4GH Council, consisting of the Executive Committee, Strategic Leadership Committee, and Product Steering Committee, guides our collaborative, globe-spanning alliance.
The Funders Forum brings together organisations that offer both financial support and strategic guidance.
The EDI Advisory Group responds to issues raised in the GA4GH community, finding equitable, inclusive ways to build products that benefit diverse groups.
Distributed across a number of Host Institutions, our staff team supports the mission and operations of GA4GH.
Curious who we are? Meet the people and organisations across six continents who make up GA4GH.
More than 500 organisations connected to genomics — in healthcare, research, patient advocacy, industry, and beyond — have signed onto the mission and vision of GA4GH as Organisational Members.
These core Organisational Members are genomic data initiatives that have committed resources to guide GA4GH work and pilot our products.
This subset of Organisational Members whose networks or infrastructure align with GA4GH priorities has made a long-term commitment to engaging with our community.
Local and national organisations assign experts to spend at least 30% of their time building GA4GH products.
Anyone working in genomics and related fields is invited to participate in our inclusive community by creating and using new products.
Wondering what GA4GH does? Learn how we find and overcome challenges to expanding responsible genomic data use for the benefit of human health.
Study Groups define needs. Participants survey the landscape of the genomics and health community and determine whether GA4GH can help.
Work Streams create products. Community members join together to develop technical standards, policy frameworks, and policy tools that overcome hurdles to international genomic data use.
GIF solves problems. Organisations in the forum pilot GA4GH products in real-world situations. Along the way, they troubleshoot products, suggest updates, and flag additional needs.
GIF Projects are community-led initiatives that put GA4GH products into practice in real-world scenarios.
The GIF AMA programme produces events and resources to address implementation questions and challenges.
NIF finds challenges and opportunities in genomics at a global scale. National programmes meet to share best practices, avoid incompatabilities, and help translate genomics into benefits for human health.
Communities of Interest find challenges and opportunities in areas such as rare disease, cancer, and infectious disease. Participants pinpoint real-world problems that would benefit from broad data use.
The Technical Alignment Subcommittee (TASC) supports harmonisation, interoperability, and technical alignment across GA4GH products.
Find out what’s happening with up to the minute meeting schedules for the GA4GH community.
See all our products — always free and open-source. Do you work on cloud genomics, data discovery, user access, data security or regulatory policy and ethics? Need to represent genomic, phenotypic, or clinical data? We’ve got a solution for you.
All GA4GH standards, frameworks, and tools follow the Product Development and Approval Process before being officially adopted.
Learn how other organisations have implemented GA4GH products to solve real-world problems.
Help us transform the future of genomic data use! See how GA4GH can benefit you — whether you’re using our products, writing our standards, subscribing to a newsletter, or more.
Join our community! Explore opportunities to participate in or lead GA4GH activities.
Help create new global standards and frameworks for responsible genomic data use.
Align your organisation with the GA4GH mission and vision.
Want to advance both your career and responsible genomic data sharing at the same time? See our open leadership opportunities.
Join our international team and help us advance genomic data use for the benefit of human health.
Discover current opportunities to engage with GA4GH. Share feedback on our products, apply for volunteer leadership roles, and contribute your expertise to shape the future of genomic data sharing.
Solve real problems by aligning your organisation with the world’s genomics standards. We offer software dvelopers both customisable and out-of-the-box solutions to help you get started.
Learn more about upcoming GA4GH events. See reports and recordings from our past events.
Speak directly to the global genomics and health community while supporting GA4GH strategy.
Be the first to hear about the latest GA4GH products, upcoming meetings, new initiatives, and more.
Questions? We would love to hear from you.
Read news, stories, and insights from the forefront of genomic and clinical data use.
Publishes regular briefs exploring laws and regulations, including data protection laws, that impact genomic and related health data sharing
Translates findings from studies on public attitudes towards genomic data sharing into short blog posts, with a particular focus on policy implications
Attend an upcoming GA4GH event, or view meeting reports from past events.
See new projects, updates, and calls for support from the Work Streams.
Read academic papers coauthored by GA4GH contributors.
Listen to our podcast OmicsXchange, featuring discussions from leaders in the world of genomics, health, and data sharing.
Check out our videos, then subscribe to our YouTube channel for more content.
View the latest GA4GH updates, Genomics and Health News, Implementation Notes, GDPR Briefs, and more.
22 Oct 2019
The Tool Registry Service (TRS) API is one of a series of technical standards from the Cloud Work Stream that together allow genomics researchers to bring algorithms to datasets in disparate cloud environments, rather than moving data around.

Image Credit: Stephanie Li, GA4GH
The GA4GH Cloud Work Stream has released a standard API for exchanging tools and workflows to analyze, read, and manipulate genomic data. The Tool Registry Service (TRS) API is one of a series of technical standards from the Cloud Work Stream that together allow genomics researchers to bring algorithms to datasets in disparate cloud environments, rather than moving data around.
Genomics tools and workflows are currently developed for use within a specific cloud environment and are typically stored in a registry that services only the associated platforms. Since each registry requires the tools and workflows it stores to meet a unique set of criteria (i.e., hardware requirements, availability of programs and their software dependencies), the contents of one registry are not guaranteed to work across multiple cloud environments. Users, such as researchers who want to replicate data from a previous study, often need access to tools originally developed to work within cloud platforms other than the one on which they manipulate their own data. This lack of interoperability slows the process and limits the variety of analyses that researchers can perform.
“It is a waste of time and resources,” said Brian O’Connor, co-lead of the Cloud Work Stream and Director of the Computational Genomics Platform at the University of California, Santa Cruz. “Developers are building multiple versions of the same exact tool to fit the standards of each individual registry in which they want it to run.”
TRS was built to address this problem by putting containerized tools (and workflows that string them together) front and center. The team both distributes and encourages the use of containerized technologies, like Docker, which allow researchers to package up tools and dependencies in an environment that can easily be moved around and used on a wide variety of platforms. With containers, researchers no longer need to worry about how users will configure or install their software.
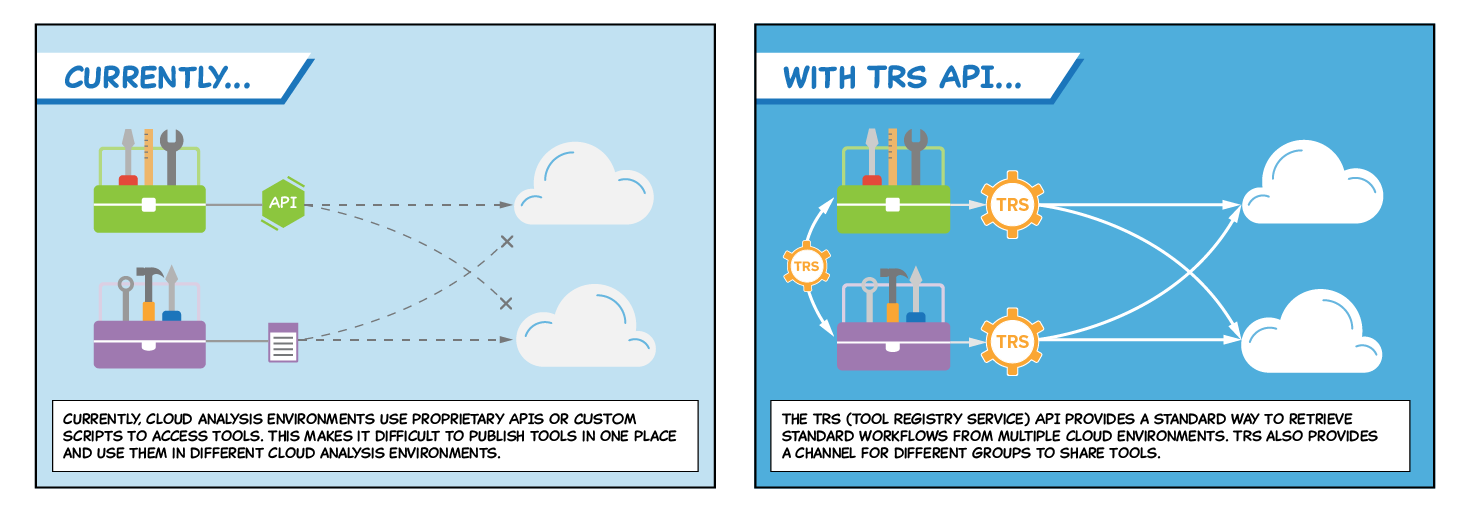
TRS also provides a standard mechanism to list, search, and register tools and workflows across multiple registries. Importantly, TRS supports tools and workflows described by the Common Workflow Language (CWL), the Workflow Description Language (WDL), and Nextflow—three of the most widely used workflow languages for running analyses on genomic data, each of which has been adopted by a different subset of institutions.
According to David Glazer, co-lead of the Cloud Work Stream and Engineering Director at Verily Life Sciences, “TRS makes tools more valuable, by making it easy to run them on more data in more environments.”
The API can also serve as a bridge between two tool registries, allowing information to be exchanged between them to better serve the user in running tools or workflows. If two tool registries hosting two different sets of tools have both implemented TRS, the registries can communicate tool information with one another. This allows a researcher whose platform only supports one of the registries to use tools listed in the other registry. TRS does this while still making it easy for users to find full documentation of the tool or workflow and contact the tool developer if they have questions about using or altering the capabilities of the tool.
TRS not only gives researchers access to far more tools than they presently have; it allows developers to register their products so that they are visible on a multitude of sites, expanding their audience reach. The API also provides a set of requirements for tool and workflow registries to implement TRS. Two major genomics tool- and workflow-sharing platforms, Dockstore and BioContainers, have implemented the API. This allows tools from Dockstore and BioContainers to be read from TRS and deployed to platforms such as Terra, DNAStack, and ELIXIR.
“The TRS API gives tool developers and users a level of tool discovery and interoperability that previously didn’t exist,” said Glazer.
The interoperability enabled by TRS is not exclusively between cloud workflow execution platforms, however. TRS was built to work in conjunction with other APIs developed by the GA4GH Cloud Work Stream. Cloud APIs, such as the recently-approved Workflow Execution Service (WES) and the proposed Data Repository Service (DRS), are part of the Work Stream’s larger goal to facilitate secure and simple data analysis, transfer, and access across many cloud environments.